PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
4800-94-6 (Disodium)
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
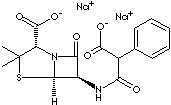
(2S,5R,6R)-6-(2-carboxylate-2- phenylacetamide)- 3,4-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylate, disodium salt;
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
· Carbenicillin: Carboxybenzylpenicillin antibiotic effective against gram-negative bacteria (such as susceptible strains of Pseudomonas species, Proteus species, Escherichia coli, and Haemophilus influenzae) and gram-positive pathogens. It is administered intramuscularly or intravenously as it is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is an analog to ampicillin.
· Carbenicillin disodium: the disodium salt of carbenicillin; slightly yellow powder; freely soluble in water; administered intramuscularly or intravenously. The chemical designation is (2S,5R,6R)-6-(2-carboxylate-2- phenylacetamide)- 3,4-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylate, disodium salt.
· Carindacillin sodium (Carbenicillin indanyl sodium): the sodium salt of the indanyl ester of carbenicillin; administered orally. The chemical designation is 1-(5-Indanyl)-N-(2-carboxy-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo- 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] hept-6-yl)-2-phenylmalonamate monosodium salt.
· Carfecillin sodium (Carbenicillin phenyl sodium) : the sodium salt of the phenyl ester of carbenicillin.
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
pass
770 (µg/mg), Anhydrous basis
WATER
6.0% max